005: Genetic Algorithms I
What is GAs
GAs are algorithms used for heuristic1 search and it is based on the evolutionary ideas of natural selection and genetics.
The building blocks of GA was presented by John Holland in the 1960s.
Terminology
- Chromosome
- Genes
- Genome
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Crossover
- Mutation
- Fitness
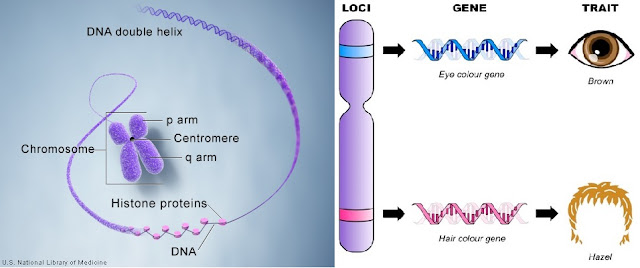
All living organisms consist of millions of cells, and each cell's nucleus of the organism contains the same set of one or more pairs of chromosomes. It is made up of tightly coiled DNA strings (il. 01), held by proteins called histones, which is visible - under a microscope - only when the cell is dividing by processes denominated mitoses and meioses.
The chromosome can be conceptually divided into loci (il. 02) (i.e. a fixed position on a chromosome), and for each locus, there is a gene2 - each of which encodes a particular protein -.
The complete set of DNA is called genome. The term genotype refers to the particular set of genes, and the physical and mental characteristics, such as eye color, height, brain size, etc..., is called phenotype.
Living organism > Cell > Nucleus > Chromosomes > DNA
The chromosome can be conceptually divided into loci (il. 02) (i.e. a fixed position on a chromosome), and for each locus, there is a gene2 - each of which encodes a particular protein -.
The complete set of DNA is called genome. The term genotype refers to the particular set of genes, and the physical and mental characteristics, such as eye color, height, brain size, etc..., is called phenotype.
|
| [Ilustration 01] Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine - " What is a chromosome? " [Ilustration 02] Source: google images... - Representation of chromosomes loci. |
Organisms whose chromosomes are arrayed in pair are called diploid; organisms whose chromosomes are unpaired are called haploid (il. 03). In nature, most sexually reproducing species are diploid, including the human being, who each have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each somatic cell3 in the body.
During eukaryote reproduction (i.e. meiosis), crossover occurs, exchanging genes between the pairs of maternal and paternal chromosomes to form gametes. The male gamete, then, fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote (a diploid cell - il. 04).
Opposing is prokaryote reproduction, which can be compared to eukaryote's mitosis4.
In this process (binary fission), during the copy of the chromosome, there is a chance that errors occur; so-called mutations (il. 05), in which single nucleotides (elementary bits of DNA) are changed. The fitness of the organism is typically defined as the probability that the organisms will live to reproduce or a function of the number of offspring the organism has (fertility).
In genetic algorithms, the term chromosome typically refers to a candidate solution to a problem, often encoded as a bit string. The "genes" are either single bits or short blocks of adjacent bits that encode a particular element of the candidate solution. An allele in a bit string is either 0 or 1. Crossover typically consists of exchanging genetic material between two single chromosome haploid parents; mutation consists of flipping the bit at a randomly chosen locus.
Most applications of genetic algorithms employ haploid individuals, particularly single chromosome individuals. The genotype in a GA using bit strings is simply the configuration of bits in that individual's chromosome. Often there is no notion of phenotype in the context of GAs.
During eukaryote reproduction (i.e. meiosis), crossover occurs, exchanging genes between the pairs of maternal and paternal chromosomes to form gametes. The male gamete, then, fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote (a diploid cell - il. 04).
 |
| [Ilustration 03] Source: Quora - "How are diploid cell structured?" [Ilustration 04] Source: Learn Genetics - "Using Karyotypes to Diagnose Genetic Disorders" |
In this process (binary fission), during the copy of the chromosome, there is a chance that errors occur; so-called mutations (il. 05), in which single nucleotides (elementary bits of DNA) are changed. The fitness of the organism is typically defined as the probability that the organisms will live to reproduce or a function of the number of offspring the organism has (fertility).
 |
| [Ilustration 05] Source: Wikipedia - Representation of the process if binary fission. |
In genetic algorithms, the term chromosome typically refers to a candidate solution to a problem, often encoded as a bit string. The "genes" are either single bits or short blocks of adjacent bits that encode a particular element of the candidate solution. An allele in a bit string is either 0 or 1. Crossover typically consists of exchanging genetic material between two single chromosome haploid parents; mutation consists of flipping the bit at a randomly chosen locus.
| [Ilustration 06] Source: Quora - "What are the chromosome mutations?" |
Most applications of genetic algorithms employ haploid individuals, particularly single chromosome individuals. The genotype in a GA using bit strings is simply the configuration of bits in that individual's chromosome. Often there is no notion of phenotype in the context of GAs.

Comentários
Postar um comentário